- Jun 5, 2023
- 10 minutes
-
 Louis de Gaste
Louis de Gaste -
 Khalil Elleuch
Khalil Elleuch -
 Yohann Doillon
Yohann Doillon -
 Dr. Áron Horváth
Dr. Áron Horváth -
 Sven Brieden
Sven Brieden
Introduction
In 2021, the NYU Stern School of Business published a cross-studies report showing a clear correlation between ESG scores and financial performances in large corporations. This meant that a successful investment strategy could not ignore those parameters. We discovered at Unit8 that being at the forefront of ESG intelligence is primarily a data engineering challenge. We want to share our best practices and how we intend to reshape the industry.
What is ESG Investing, and why does it matter?
Figure 1: ESG Components
Environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing is an investment strategy that considers environmental, social, and governance metrics of assets alongside financial factors to generate long-term financial returns while promoting positive social and environmental outcomes. The metrics used typically include an evaluation of the CO2 emissions or other forms of pollution, respect for human rights, promotion of social inclusion, the structure of the board of directors, or audit practices.
ESG Regulations and Compliance
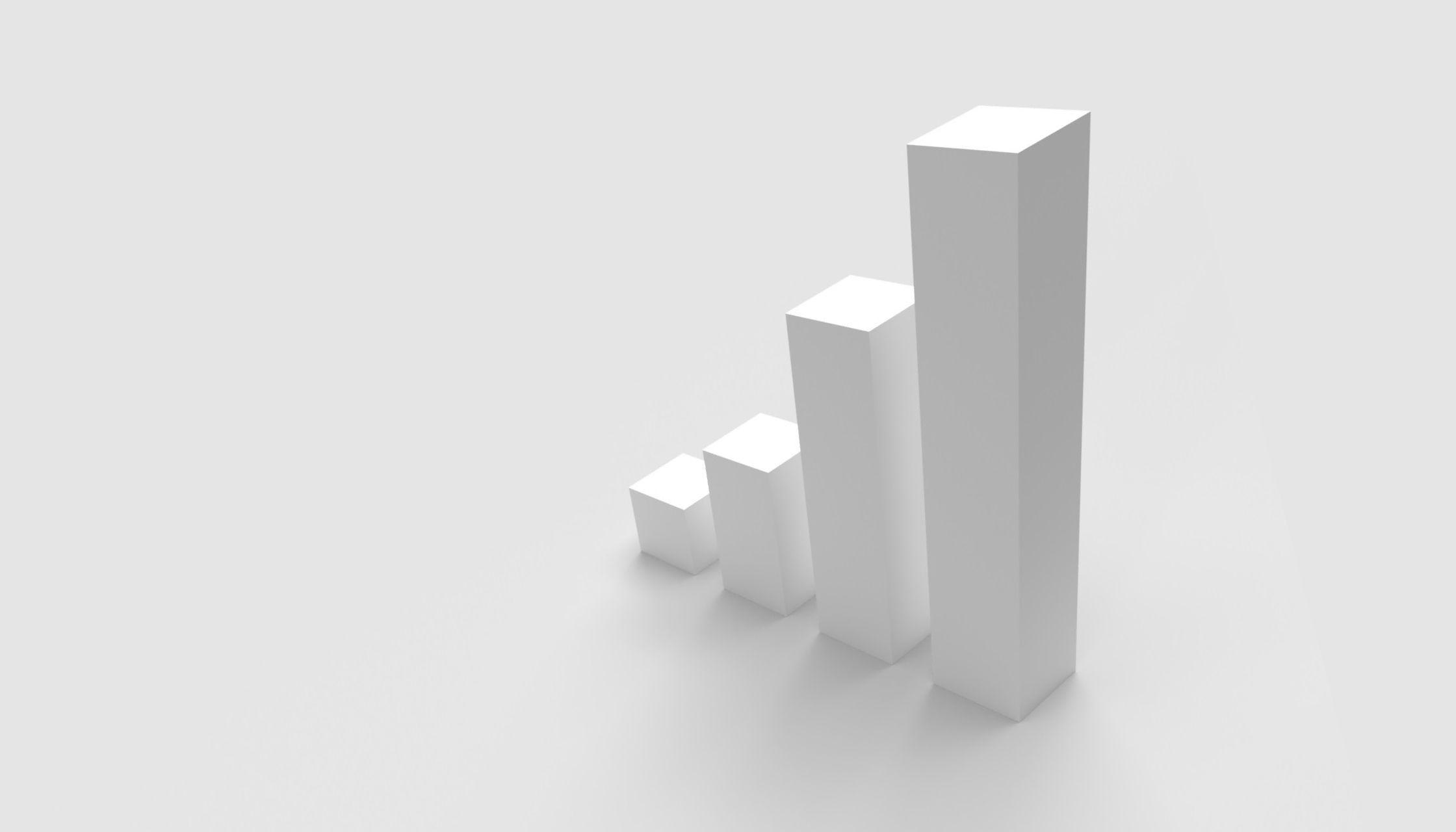
ESG investing has recently gained considerable popularity as its financial relevance has become more prominent. Beyond the positive economic consequences of good environmental and social practices, the relation between a company’s performance and its ESG scores is amplified by regulations intended to transform the industry. We see the emergence of both incentivising laws (e.g., carbon credits[1], 2022 US IRA[2]) and deterring regulations (EU ETS[3], CSDD[4]), which can make or break the financial viability of companies depending on their ESG performances. This impact will become even more dominating in the years to come as the rate of new regulations passed per year increases all over the world[5].
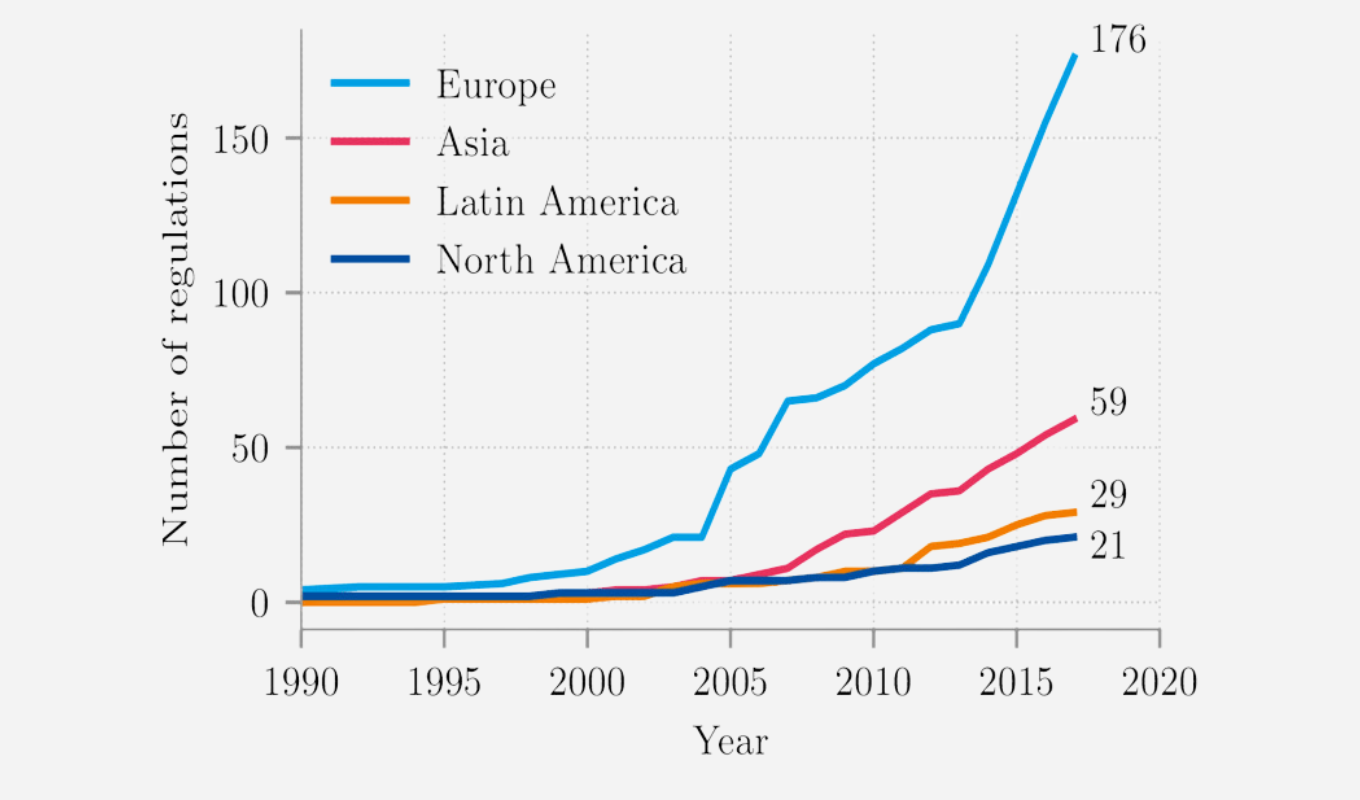
Figure 2: Number of new ESG regulations passed across the world
On top of making ESG factors even more financially relevant, regulations are also set to improve the ESG investing efficiency by changing the reporting practices. A number of legislations are being introduced to make ESG reporting mandatory for large corporations like the CSRD[3] or 2022 SEC consultation[4], making more and better data available, while new reporting frameworks – such as GRI, SASB, and TCFD – facilitates the access to this data for investors.
ESG Data Challenges
Manipulating and accessing ESG data represents a uniquely complex challenge. From our experience, the heart of the problem lies in contrast between the highly messy ESG data sources and the high-reliability needs of the banking industry.
Sourcing the data
Investors do not process thousands of company reports themselves to build their intelligence, but instead buy it from specialized data brokers that have processed the data into tabular reports. The market is dominated by 3 main providers – MSCI, ISS and Sustain analytics accounting for 60% of the market share -, with a multitude of smaller ones sharing the remaining 40%[6].
Such a diversified pool of providers, with various industries, geographies and business models, suffers from a total lack of standardization between the products, whether it is in the methodology or in the data structure. We observe for example that different providers use different weights in their metric aggregations, resulting in inconsistent interpretations.
Analysts hence have to review and assess different methodologies. Regarding the data structure, there are 4 main challenges to tackle:
- No consistency in file formatting (which are generally very large CSVs or Excel files);
- Varying refresh rates;
- Common human errors induced between data refreshes;
- Missing values
The fast changes in the ESG landscape, driven by new reporting regulations, add yet another challenge and any data ingestion solution must be designed to be exceptionally flexible. It’s clear that data in the near future will be very different and traditional data processing practices are much too rigid to adapt efficiently to those changes.
Data Quality Issues
Data quality represents the most challenging part of the problem. While ESG data sourcing is a complex engineering task, it’s at least easy to monitor if it’s done correctly. We do not have this luxury when ensuring the data quality because erroneous data points can be ingested silently by the pipeline and find their way to the report. This is a critical problem as financial institutions must comply with audits, which means inaccurate reports have not only enormous financial and legal implications. Furthermore, we observe that ESG data has particularly bad data reliability since it is based mainly on manual data creation.
The traditional solution would be to have a very conservative strategy and drop any data deviating slightly from what is expected. This, however, represents a significant loss of value in a highly competitive market, especially considering the cost of these data sources. This means we have to recover everything that is recoverable and filter out everything that’s beyond recoverable with no margin of error. In essence, we are pushing the data quality management task to its absolute limit.
Zoom-in: the problem of unresolved entities
“I want to find all the ESG information related to company X”. This requirement is an excellent case study to illustrate the problems arising from ESG data. It is a notoriously simple task (known as SELECT WHERE) which becomes very complex in the case of ESG.
The solution would generally be to look up the company ID (or ISIN) across the whole data and collect the related rows. Not only does this fail to match 10 to 40% of the results, but it also fails at different levels, ranging from a data format issue to disagreement across sources on defining the company. For example, other providers may either use multiple ISINs or a common ISIN to refer to the different share classes of a large company. On top of this, not all sources cover all companies meaning that we don’t know in advance how many matches we would expect.
This task, which would typically be a 5-minute job, becomes a multi-day project in the case of ESG data. This demonstrates the magnitude of the challenges ahead, considering that making solid investment decisions requires much more complex data analysis.
Unit8 Solutions
“There is no problem that doesn’t have a solution”.
Fortunately, our years of experience have shown us that this saying also holds true for ESG investing. The best thing Unit8 can do is to share some of the knowledge gained along the way.
Experience is key
When a data engineer/ scientist joins a project in finance for the first time, they always have to reevaluate their previous work methods. In banking, end-users are considerably data-aware, products must be absolutely resilient, environments are tightly controlled, communication has to be detailed, etc. That’s why each new project in finance will benefit significantly from the experience accumulated from the previous ones.
This specialized way of doing data projects starts at the very beginning when defining the scope of the project:
- Requirements must be specifically described in a way that matches the high-reliability needs of the client.
- More resources than usual must be estimated to reach the milestones.
- The overhead bureaucracy to get access to data and development environments must be more strongly anticipated to avoid wasting the first weeks of work.
To ensure a successful project, similar changes to the usual ways of working must be done at every stage and implementing them correctly requires a deep understanding of the clients’ needs and priorities, which only years of hands-on experience can provide.
Reconciling ESG Data sources
Bringing together the data from all the providers and all their products relies on this deep understanding of the client’s priorities. We’re working with data that is sometimes missing, sometimes overlapping and often disagreeing. In “normal” industries, the solution involves the creation of reconciliation and aggregation methods to ensure that end-users do not have to confront the messy reality of the data.
However, the paradigm is very different in the banking industry. In our experience, the end-users are much more comfortable with working with data but cannot afford approximations in the data processing. Although an aggregated layer can be a nice-to-have feature, it is more essential to ensure that the end user can navigate the raw data efficiently and have all the contextual information (sources, definitions, etc.). The idea that “more data is better than fewer data” also applies to missing values: insights can still be provided to the user by showing related or contextual information when a value is missing (e.g. for missing numbers on a subsidiary, provide the data inherited from the parent company).
Improving Data Quality
Data hub projects often neglect the data validation framework because priority is always given to reaching MVP status and developing new features. Ultimately, there is never a “right time” to tackle this task. That’s unacceptable in ESG data because it is the core of the strategy to ensure reliable reports. When tackling the data validation framework, a few reality checks must be accepted:
In finance, it’s not acceptable to shortcut data validation → The data validation needs to have its own KPIs and be part of the requirements to make sure it’s done correctly.
Data validation needs a larger amount of resources → This task involves thorough data exploration and a complete knowledge of each column’s behaviour is needed to define the checks. The complexity can grow exponentially if cross-source checks are needed.
Quality reports and notifications will be part of the framework → Product owners must be informed about current data quality issues and how they evolve, and they need to have all the necessary documentation to evaluate their data providers.
Implementing an entity resolution solution
Avoiding approximations at all costs is the driving principle to solve the entity resolution problem. Among the hundreds of columns in raw data, several of them can be used as proxies for the ID of a company. However, different proxies might disagree on how to match companies across sources. Instead of comparing the matches and automatically selecting the “best” one, it is favorable to create a solution that can handle multiple matching scenarios and display all the results to the analyst. As a consequence, the interface should be adapted to navigate clearly the excess of data and at the same time provide the analyst the possibility to discard results they are not interested in.
Unit8 vision
Building on the experience gained over multiple projects with 5 different banks, Unit8’s vision is centered around scaling-up the usage of data in the ever-changing world of ESG investing. By harnessing our expertise in data management, technology, and industry knowledge, Unit8 aims to empower investors and organizations to make informed decisions that align with their values and contribute to a sustainable future.
Replicable Approach to ESG Integration
Despite the lack of uniformity in ESG data, we believe that improving the ESG-investing landscape requires a replicable approach that can then be tailored to different use-cases while addressing common concerns and interests. Our focus lies in key dimensions such as CO2 emissions, respect for human rights in high-risk areas, and regulatory compliance, which are essential components in the ESG space.
Taking the initiative to bring changes, we are developing a solution in partnership with Palantir Foundry to provide reliable, efficient and customizable access to ESG data for investors and analysts. Adapting the front-end to the habits of our customers, we designed two different interfaces:
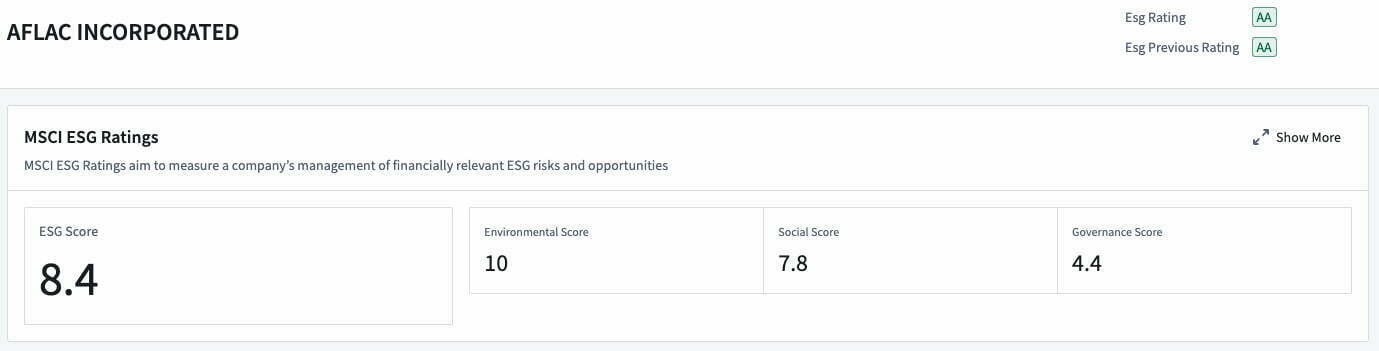
- A company-level aggregation which offers detailed ESG data collected from multiple data providers to enable an in-depth, single-company analysis.
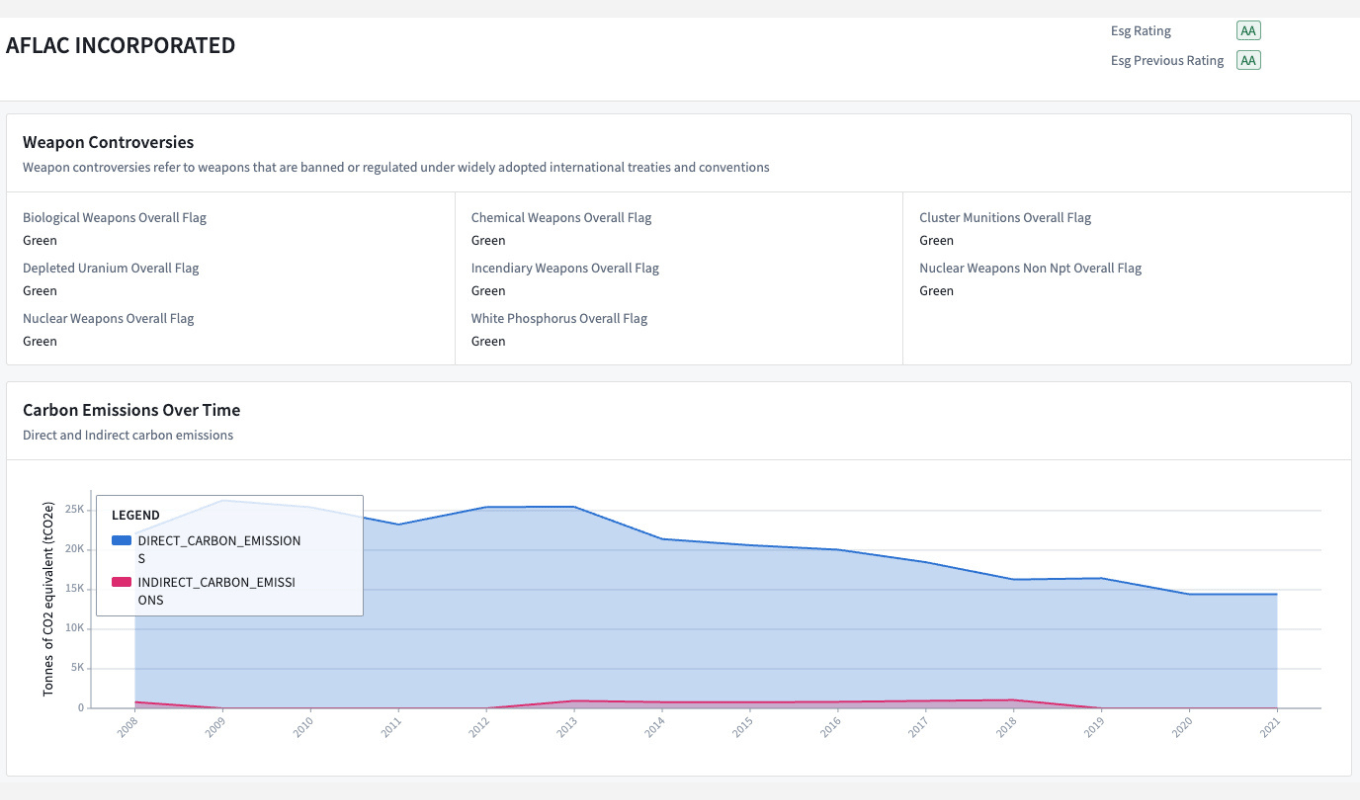
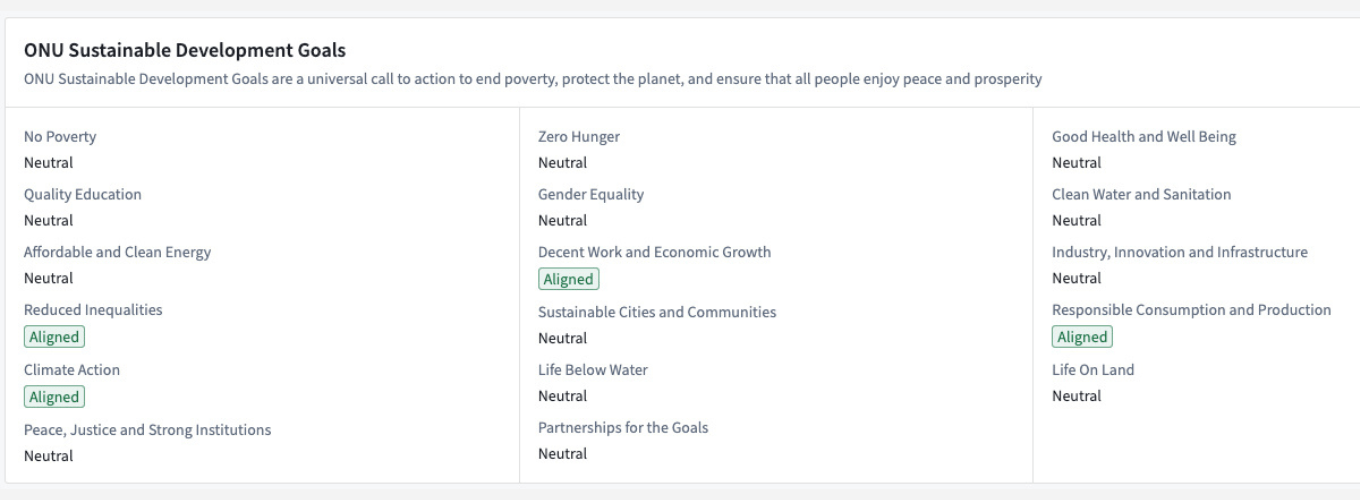
- A portfolio-level aggregation which provides an overview of the ESG exposure of a portfolio and an analytical support in creating portfolios matching ESG criterions
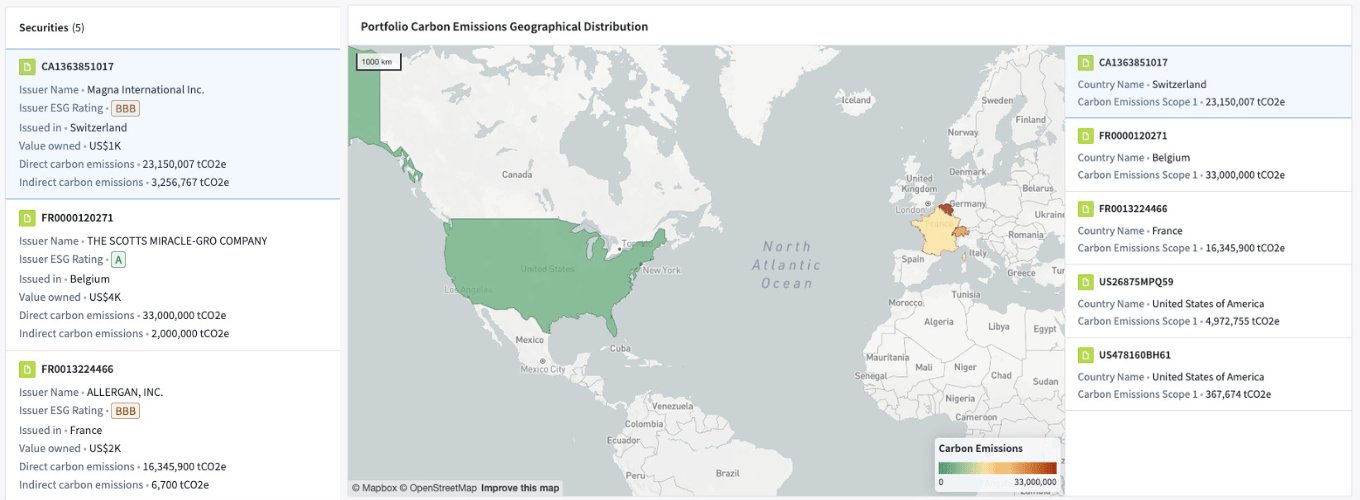
Although being a product in development which will integrate many more features, it already implements the core principles of delivering high quality data for ESG investing: With this application we provide easy-to-navigate, high level aggregation while enabling a fully transparent exploration of the core data.
Leveraging wide Data capabilities to stay ahead
Because we know that a one-size-fits-all product can never be the whole solution to accessing ESG data access, we aim to stay a reliable and versatile partner by continually developing our data processing and visualization capabilities. At Unit8, we believe that our strength lies not in the tools we use, but in the people who can adapt to the new challenges. Currently, our broad technological expertise allows us to adapt to the unique infrastructure and constraints of each client, ensuring seamless integration with a wide range of data platforms such as AWS, Azure, Snowflake, and Oracle. We do not expect to see the emergence of a single “one size fits all” solution in the near future, that’s why we are consolidating and expanding our scope of capabilities.
Our commitment to a knowledge-sharing culture further enhances our ability to provide innovative and effective ESG solutions. We foster an environment that encourages projects and asset documentation, employee education sessions, and collaboration between experts and industry practitioners. This continuous exchange of ideas and best practices enables Unit8 to stay at the forefront of the ESG landscape, delivering tailored and scalable solutions that drive sustainable progress for our clients and the world at large.
Let’s get to work!
At Unit8, we are committed to pushing the field of ESG investing forward because we believe it is the most promising way to reconcile sustainability and financial efficiency. However, its potential can only be unlocked when all the actors of the financial market have reached ESG maturity. As a provider of data solutions, our main lever for impact is by supporting companies in improving their analytics capabilities. Therefore, our strategy to influence the ESG market is by pushing the standards of ESG intelligence.
If you want to take part in this transformation, we would be happy to explore how we can support you in creating value and sustainability. So let’s get in touch, we are excited to start working with you!





