- Aug 23, 2023
- 5 minutes
-
 Andreas Blum
Andreas Blum -
 Thanos Giannakopoulos
Thanos Giannakopoulos
Never has there been more demand for generative AI since the arrival of ChatGPT 3.5 in late 2022 – and the market shows no signs of letting up. More and more Swiss companies are leveraging this technology in creative ways to add customer value (e.g. Helvetia’s Clara chatbot, Zurich Insurance, Vivi Kola). But, from its limitless applications, which use case(s) is the Swiss market choosing to implement first? “Vanilla” ChatGPT, “Chatable” Knowledge Base, Insight Extraction, Content Generation and the list goes on. Over the last six months, we’ve collected insights from discussions and workshops with key data decision-makers. In this article, we unpack those insights and explore the four most often requested Generative AI use cases.
“Vanilla” ChatGPT
In a nutshell, this is ChatGPT without its notorious data sharing. By leveraging Azure’s OpenAI Service, it can provide full ChatGPT functionality to employees but with no data being communicated to Microsoft nor OpenAI. Notably, this use case is more of a risk limiter than a value adder. It’s perfect for companies who wish to mitigate the risk of a potential data leak, like the one at Samsung. It’s also a great starting point for companies looking to try out GenAI and safely explore its application in their business. A fine example is RocheGPT, leveraging generative functionality to accelerate drug discovery & development.
“Chatable” Knowledge Base
A “top-charting “ use case, the chat-able knowledge base, is frequently requested. Essentially, ChatGPT connects to a knowledge base, becoming the user’s primary interface. The user inputs a prompt, requesting certain information that would otherwise have to be found manually (e.g. What is the company’s updated travel policy?). The depth of ChatGPT’s response is flexible, from providing a simple index of where the relevant documents can be found to succinctly summarising key pieces of information across hundreds or thousands of documents. Companies who produce and/or operate physical goods at scale will find this use case particularly attractive since through a single prompt it can scan 1000s of targeted documents, extract the requested information from each and succinctly summarise the unstructured data found in operation manuals, warranties, safety manuals, etc.
Insight Extraction
A cousin of the “chat-able” knowledge base, this use case focuses on processing individual documents, identifying and summarising key insights for the reader. For example, these could be real estate investment documents that bank analyses on a continuous basis to find new opportunities and/or adapt investment portfolios. Instead of manually having to extract the relevant pieces of information, the model provides a summary allowing for a faster go/no-go decision to be made. When pursuing this use case consider that the model typically undergoes some fine-tuning during implementation. The reason being is you’ll want to improve its accuracy especially if frequent, business-critical decisions are made based on the insights the model extracts.
Content Generation
From text to visuals to protein sequencing, this use case is the most versatile. Depending on its complexity, it can be very straightforward; a case in point would be marketing & sales using ChatGPT with a “human-in-the-loop” approach to draft/automate emails, social media posts, and other client-facing documents. On the other hand, a use case could be exploring and reformulating molecular compositions of products to optimise for product-market fit, raw material costs or sustainability. This use case is generally requested by companies who already have a confident foothold in the AI space and have integrated the technology into a well-oiled process.
Conclusion
From the workshops and discussions, we propose three questions that key data decision-makers must ask themselves before embarking on their first GenAI use case. First, can the use case be easily communicated, explained and understood by the rest of the organisation? From our own experience, introducing AI into your employees’ working lives requires patience and ease; it’s best to start with a use case that’s easy to grasp. The journey will have a smoother start if everyone on board knows what the vision is, what the fundamentals of GenAI are and why it’s the chosen method to achieve that vision. Second, can the use case be considered low-risk? This is a multifaceted question where one needs to understand what the business ramifications of a successful or failed implementation are, the degree of regulatory compliance one must abide by, the degree of data sensitivity and its corresponding damage potential. Lastly, can the use case be implemented quickly and does it have a noticeable impact? For the successful implementation of subsequent use cases, it is vital to gain momentum by securing early wins with high notoriety. On that note, we offer the following roadmap below to help guide your next GenAI decision.
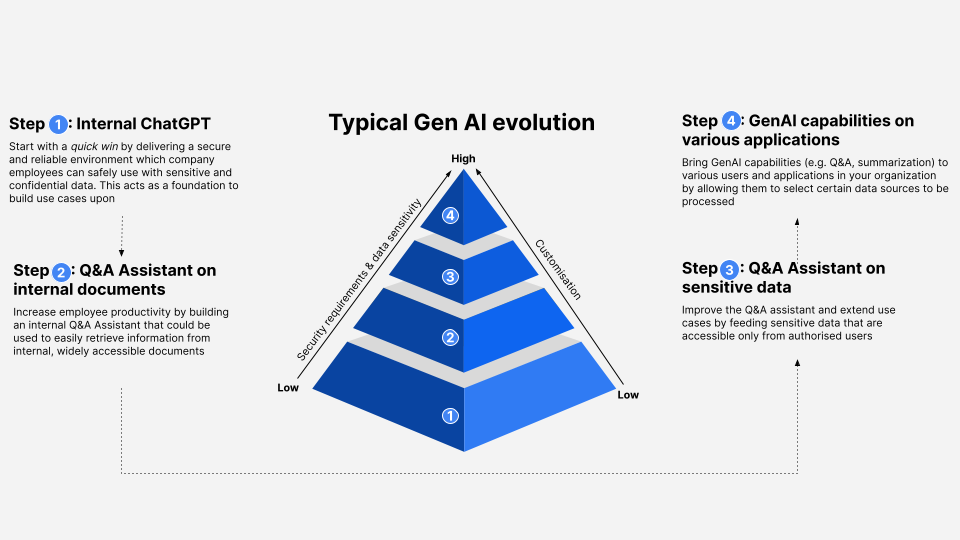
We hope this inspired you to consider generative AI in your own organization and if you’re looking for a general orientation on AI, or how to get started with GenAI then don’t hesitate to reach out to us.